Oral hygiene instructions are essential for maintaining dental health, while dental codes like D1330 standardize procedures․ Proper coding ensures accurate billing and effective patient care delivery․
1․1 Overview of Oral Hygiene Practices
Oral hygiene practices are essential for maintaining healthy teeth and gums․ These practices include daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and interdental cleaning to remove plaque and food particles․ Proper brushing technique involves using a fluoride toothpaste and brushing for at least two minutes, twice a day; Flossing helps clean areas between teeth that a toothbrush cannot reach․ Special oral hygiene aids, such as interdental brushes or mouthwash, may also be recommended for specific needs․ Regular dental exams and cleanings further support overall oral health․ These practices help prevent issues like tooth decay and gum disease, promoting long-term dental well-being․
1․2 Importance of Dental Codes in Oral Hygiene
Dental codes, such as the D1330 code, play a crucial role in standardizing oral hygiene instructions․ These codes ensure consistency in documentation, billing, and insurance claims․ Proper use of dental codes helps dental professionals communicate effectively about patient care, ensuring that treatments are tracked accurately․ This standardization also aids in evaluating the effectiveness of oral hygiene practices and improves patient outcomes․ By using specific codes like D1330, dental teams can efficiently manage patient records and billing processes, contributing to a well-organized and efficient healthcare system․ Accurate coding supports compliance with regulatory requirements and enhances overall patient care quality․
Understanding the D1330 Dental Code
The D1330 code pertains to oral hygiene instructions, covering tooth brushing, flossing, and special aids․ It ensures personalized care plans are effectively documented and billed․
2․1 What is the D1330 Code?
The D1330 code refers to oral hygiene instructions provided by dental professionals․ It includes guidance on tooth brushing techniques, flossing, and the use of special oral hygiene aids․ This code is used to document personalized patient education, ensuring proper home care routines are established․ It is a standardized way to bill for the time spent on educating patients about maintaining their oral health․ The D1330 code is essential for promoting preventative care and ensuring patients understand how to manage their dental hygiene effectively․ It is widely recognized in dental practices for its role in improving patient outcomes and adherence to oral health routines․
2․2 When to Use the D1330 Code
The D1330 code is used when dental professionals provide personalized oral hygiene instructions to patients․ This includes scenarios such as during patient visits, new diagnoses, or when updating care plans․ It applies to educating patients on proper tooth brushing techniques, flossing, and the use of special oral hygiene aids․ The code is appropriate for both new and existing patients who require tailored guidance to improve their oral health․ It is essential to use this code when the instruction is specific to the patient’s needs and not part of a routine exam or cleaning․ Proper documentation ensures accurate billing and reflects the personalized care provided․
2․3 Documentation Requirements for D1330
Accurate documentation is crucial when using the D1330 code for oral hygiene instructions․ Records must include the patient’s name, date of service, and detailed notes on the instructions provided․ Specifics such as tooth brushing techniques, flossing methods, and recommendations for special oral hygiene aids should be clearly outlined․ The documentation should also reflect the patient’s understanding and any follow-up plans․ Proper documentation ensures compliance with billing standards and demonstrates the personalized care provided․ It is essential to maintain thorough records to support the use of the D1330 code effectively․

Oral Hygiene Instructions for Patients
Oral hygiene instructions provide personalized advice on tooth brushing, flossing, and using special aids to maintain dental health and prevent oral diseases effectively․

3․1 Tooth Brushing Techniques
Proper tooth brushing involves using a fluoride toothpaste and brushing gently in circular motions for two minutes, twice daily․ This technique helps remove plaque effectively without harming gums․ Patients should pay special attention to areas where teeth and gums meet, ensuring all surfaces are covered․ Electric toothbrushes can enhance cleaning for some individuals․ Demonstrating the correct method and addressing common mistakes, like brushing too hard, can improve oral hygiene outcomes․ Regular reviews of brushing technique during dental visits ensure patients maintain good habits and adapt as needed for optimal dental health․
3․2 Flossing and Interdental Cleaning
Flossing is crucial for removing plaque and food particles between teeth and under the gumline, where a toothbrush cannot reach․ Daily flossing prevents gum disease and cavities by eliminating trapped debris․ Proper technique involves gently curving the floss around each tooth in a “C” shape and sliding it up and down․ Interdental cleaning tools, like floss picks or brushes, are effective for larger spaces․ These methods complement brushing, ensuring a thorough oral hygiene routine․ Regular flossing and interdental care are vital for maintaining healthy gums and preventing dental issues, aligning with the importance of accurate documentation in dental coding practices․
3․3 Use of Special Oral Hygiene Aids
Special oral hygiene aids, such as mouthwash, interdental brushes, and dental floss, are designed to target areas traditional brushing misses․ Mouthwash can reach deep pockets and disinfect, while interdental brushes clean between tightly spaced teeth․ These tools are particularly useful for patients with specific oral health needs, such as those with orthodontic appliances or gum disease․ Proper use of these aids, as demonstrated by dental professionals, enhances plaque removal and gum health․ Regular use, combined with personalized recommendations, ensures comprehensive oral hygiene and supports the documentation required for codes like D1330․
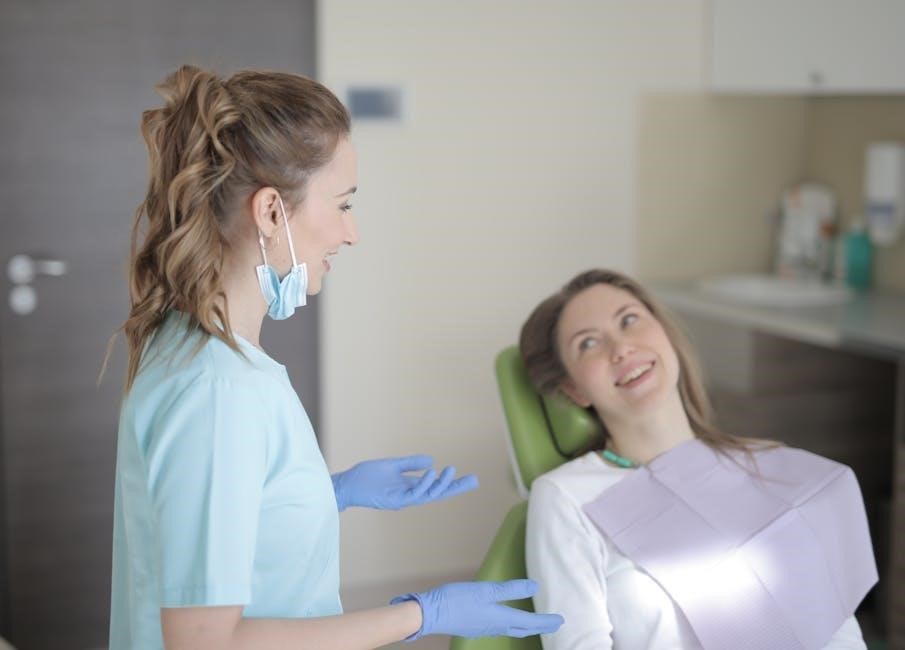

Role of Dental Professionals in Oral Hygiene Education
Dental professionals play a crucial role in educating patients on oral hygiene․ They provide personalized advice, demonstrate techniques, and empower patients to maintain optimal dental health through proper care․
4․1 One-to-One Oral Hygiene Advice
One-to-one oral hygiene advice is a personalized approach where dental professionals provide tailored guidance to patients, addressing specific needs and concerns․ This method has been shown to be effective in improving oral health outcomes․ Dental professionals demonstrate techniques, discuss individualized care plans, and educate patients on proper brushing, flossing, and the use of oral hygiene aids․ This direct interaction empowers patients to take control of their oral health, leading to better adherence to recommended practices․ Training programs for dental professionals emphasize the importance of clear communication and empathy in delivering effective one-to-one advice, ensuring patients feel supported and motivated to maintain good oral hygiene habits․
4․2 Training and Education for Dental Hygienists
Training and education for dental hygienists are crucial for delivering effective oral hygiene instructions․ Programs often include hands-on experience with phantom heads and real patients, focusing on preventing oral diseases․ These courses emphasize skills in patient assessment, personalized care plans, and proper documentation using codes like D1330․ Hygienists learn to communicate clearly, ensuring patients understand their oral health needs and how to address them․ Practical training also covers the use of fluoride, interdental cleaning, and special oral hygiene aids, equipping professionals with the tools to provide comprehensive care and empower patients to maintain optimal oral health․
4․3 Empowering Patients Through Oral Health Education
Empowering patients through oral health education enhances their ability to maintain good hygiene․ Dental professionals provide personalized advice, demonstrating techniques like brushing and flossing․ Education also covers the use of fluoride and special aids, ensuring patients understand their benefits․ By addressing barriers to care, especially in rural areas, patients gain confidence in managing their oral health․ This proactive approach not only improves hygiene habits but also fosters a long-term commitment to dental wellness, reducing the risk of oral diseases and promoting overall health outcomes․

Preventative Dentistry and Oral Health
Preventative dentistry focuses on maintaining oral health through daily brushing, flossing, and routine exams․ It emphasizes fluoride use and early detection of issues to prevent disease․

5․1 Daily Brushing and Flossing Habits
Daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste, ideally twice a day for two minutes, is crucial for removing plaque and preventing tooth decay․ Flossing once daily helps eliminate interdental plaque and debris that brushing misses․ These habits are foundational to preventative dentistry, promoting healthy teeth and gums․ Consistency in these practices reduces the risk of oral diseases and supports overall oral health․ Proper technique is key, and dental professionals often provide personalized guidance to ensure effectiveness․ Regular adherence to these routines complements professional cleanings and exams, fostering a comprehensive approach to maintaining optimal dental well-being․
5․2 Importance of Routine Dental Exams and Cleanings
Routine dental exams and cleanings are vital for maintaining oral health and preventing dental issues․ These appointments allow professionals to detect early signs of decay, gum disease, and other concerns․ Cleanings remove plaque and tartar, which brushing and flossing may miss, reducing the risk of cavities and infections․ Regular exams also enable personalized recommendations for improvement․ By addressing problems early, patients avoid costly and complex treatments later․ These visits complement daily hygiene practices, ensuring a comprehensive approach to oral care and promoting long-term dental well-being․ Consistent check-ups are a cornerstone of preventative dentistry․
5․3 Role of Fluoride in Oral Hygiene
Fluoride plays a crucial role in oral hygiene by strengthening tooth enamel and preventing decay․ It is a natural mineral found in water, toothpaste, and mouthwashes, and is proven to reduce cavity risk․ Fluoride works by remineralizing teeth, reversing early stages of decay, and making teeth more resistant to acid attacks from plaque and sugars․ Regular use of fluoride toothpaste and community water fluoridation are widely recommended․ It is especially beneficial for children’s developing teeth but also protects adult teeth․ Proper fluoride use, as guided by dental professionals, is a cornerstone of preventative oral care and promotes lifelong dental health․
Special Considerations for Oral Hygiene
Special considerations include tailored oral hygiene practices for patients with special health needs, carepartner-assisted interventions, and addressing barriers in rural or underserved communities to ensure equitable care;
6․1 Oral Hygiene for Patients with Special Health Care Needs
Patients with special health care needs require tailored oral hygiene approaches․ This includes adaptive tools, personalized routines, and carepartner assistance․ Dental professionals play a crucial role in providing customized advice and training, ensuring these patients maintain optimal oral health despite physical or cognitive challenges․ Regular monitoring and adjustments to hygiene practices are essential to address their unique conditions effectively․ Collaboration between caregivers and dental teams fosters a supportive environment, promoting long-term oral health outcomes for these individuals․
6․2 Carepartner-Assisted Oral Hygiene Interventions
Carepartner-assisted oral hygiene interventions involve training caregivers to help patients maintain oral health․ These interventions are particularly beneficial for individuals with cognitive or physical impairments․ Carepartners are taught to demonstrate proper brushing and flossing techniques, use adaptive tools, and monitor oral hygiene routines․ Programs often include hands-on training and educational resources to empower carepartners․ This collaborative approach fosters independence and confidence for both patients and caregivers․ Regular follow-ups with dental professionals ensure the effectiveness of these interventions, ultimately improving oral health outcomes for vulnerable populations․
6․3 Oral Hygiene in Rural and Underserved Communities
Oral hygiene in rural and underserved communities faces unique challenges due to limited access to dental care․ Barriers such as lack of dental facilities, transportation, and financial constraints hinder proper oral health maintenance․ Community-based programs and portable dental units can help bridge this gap․ Educational workshops and partnerships with local organizations are essential to promote oral hygiene practices․ Additionally, addressing cultural beliefs and language barriers is crucial for effective outreach․ Telehealth services and mobile clinics can extend care to remote areas․ Empowering these communities with oral hygiene knowledge and resources is vital for improving overall health outcomes and reducing disparities in dental care․

Billing and Coding Tips for Dental Teams
Accurate coding and documentation are crucial for dental billing․ Use D1330 correctly for oral hygiene instructions, follow guidelines, and avoid common errors to ensure proper reimbursement and compliance․
7․1 Best Practices for Using the D1330 Code
Using the D1330 code requires precise documentation of oral hygiene instructions provided to patients․ Ensure all interactions are recorded, including personalized advice on brushing, flossing, and special aids․ Verify patient eligibility and compliance with insurance guidelines․ Avoid overcoding by documenting only necessary services․ Train staff on accurate coding practices to prevent errors․ Regularly audit claims to ensure adherence to regulations․ Use the code only for initial or comprehensive instructions, not for routine cleanings․ Stay updated on coding changes and seek professional advice if unsure․ Proper use ensures smooth billing and maintains patient trust in dental care services․
7․2 Avoiding Common Billing Errors
To avoid billing errors with the D1330 code, ensure accurate documentation of oral hygiene instructions․ Overcoding is a common mistake, so only bill for services actually provided․ Verify patient eligibility and avoid using the code for routine cleanings․ Ensure all claims include detailed records of the instructions given, such as tooth brushing techniques or flossing guidance․ Double-check for incorrect or missing information on claims․ Avoid using non-compliant codes or bundling services improperly․ Regularly audit claims to identify and correct errors․ Proper billing practices reduce reimbursement delays and ensure compliance with dental coding standards, maintaining trust and transparency in patient care․
7․3 Real-World Documentation Examples
Documentation for the D1330 code should include detailed records of oral hygiene instructions provided․ For example, note specific tooth brushing techniques demonstrated, such as the modified Bass method, and flossing guidance․ Document any recommendations for special oral hygiene aids, like interdental brushes or mouthwash․ Include patient-specific advice, such as adjusting brushing frequency for gum disease․ Example: “Patient instructed on proper tooth brushing technique, emphasizing gentle circular motions, and flossing to remove interproximal plaque․ Recommended a fluoride mouthwash for added protection․” Such records ensure accurate billing and compliance with dental coding standards, while also providing a clear history of patient education․
Effective oral hygiene practices, combined with accurate use of dental codes like D1330, ensure optimal patient care and compliant billing, advancing oral health outcomes and professional standards․
8․1 Summary of Key Points
Oral hygiene instructions are crucial for maintaining dental health, emphasizing tooth brushing, flossing, and interdental cleaning․ Dental codes like D1330 standardize these practices, ensuring proper documentation and billing․ Effective communication between dental professionals and patients is key to adherence․ Regular dental exams and fluoride use prevent oral diseases․ Special considerations, such as care for patients with special needs and underserved communities, highlight the need for tailored approaches․ Accurate coding and billing practices ensure compliance and optimal care delivery․ Continuous education for dental teams and patients empowers healthier outcomes, aligning with the future of oral hygiene and dental coding advancements․
8․2 The Future of Oral Hygiene and Dental Coding
The future of oral hygiene and dental coding lies in advancing technology and personalized care․ Tele-dentistry will expand access to oral hygiene instructions, while AI enhances data analysis for preventive treatments․ Coding systems like CDT will evolve, incorporating real-time data for streamlined billing․ Emphasis will grow on sustainability, with eco-friendly hygiene products gaining prominence․ These advancements aim to improve patient outcomes, reduce disparities, and integrate oral health into overall well-being․ By leveraging innovation, dental care will become more efficient, patient-centric, and aligned with global health goals․